Graphic EQ
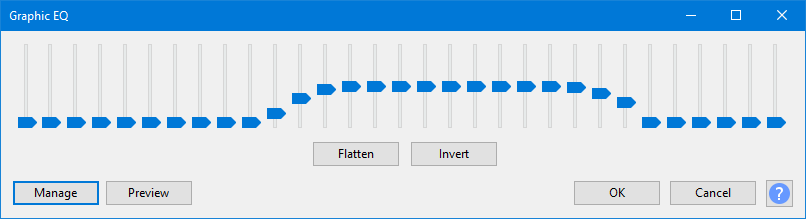
As an example of equalization, the curve defined by the slider settings below shown below changes the balance of high and low frequencies in the audio to make it sound like a telephone. High and low frequencies are filtered out.
- Accessed by:
Contents
Graphic EQ sliders
Frequency Sliders: the equalization curve is drawn by manipulating a set of sliders. Each slider adjusts the gain of a specific range of frequencies, the gain being maximized at (centered on) the frequency stated on the slider. Click and drag the slider up or down to increase or decrease the volume by a maximum of 20 dB. You can Tab between each slider. You can get to an exact slider value but the method depends to some extent on your operating system. Try:
- Clicking above or below the slider to increment it up or down by a fixed value in whole dB
- Clicking above or below the slider to jump to a nearby whole dB value
- Using the arrow keys on the keyboard to increment by 1 dB
- Holding down Shift then either dragging the slider handle or using the arrow keys to increment by 0.1 dB.
The sliders can also be made taller by resizing the dialog. This can make setting the value you want easier.
The current value of the slider can be seen by hovering over it with the mouse.
| No account is taken of whether your slider settings will result in the selection being amplified beyond the clipping (distortion) level. If your slider settings amplifies any frequencies, especially the lower frequencies which are normally the loudest, the track(s) first to -3 dB or lower. If necessary you can always the Graphic EQ, Normalize again to a lower level, then re-apply Graphic EQ. |
Equalization settings
- : A quick way to set a "level response curve". This means the curve on the graph is drawn from left to right at 0 dB on the vertical scale, so that no frequencies will have their volume level modified.
- : Turns the current curve in the window upside down, changing positive gains at a particular frequency into negative, and vice versa.
Other buttons
Clicking on the command buttons give the following results:
- gives a dropdown menu enabling you to save and restore your custom slider settings. For details see Manage presets.
- plays a short preview of what the audio would sound like if the effect is applied with the current settings, without making actual changes to the audio.
The length of preview is determined by your setting in , the default setting is 6 seconds.
- applies the effect to the selected audio with the current effect settings.
- aborts the effect and leaves the audio unchanged.
Limitations
To process Equalization, all tracks in the project must have the same sample rate. To change the sample rate of a track without affecting speed or pitch, use .